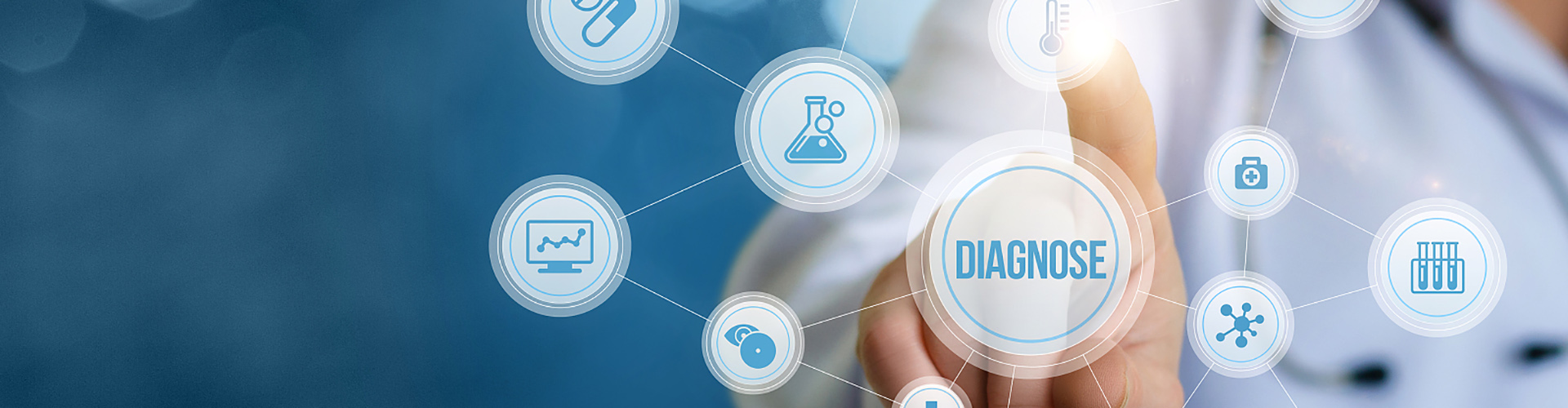
Proteinase K mNGS (liquid)
Proteinase K is a stable serine protease with broad substrate specificity. It degrades many proteins in the native state even in the presence of detergents. Evidence from crystal and molecular structure studies indicates the enzyme belongs to the subtilisin family with an active site catalytic triad (Asp39-His69-Ser224). The predominant site of cleavage is the peptide bond adjacent to the carboxyl group of aliphatic and aromatic amino acids with blocked alpha amino groups. It is commonly used for its broad specificity. This proteinase K is specially designed for mNGS. Compared with the other proteinase K, it contains even less nucleic acid contamination with the same enzymatic performance, which could better ensure the downstream mNGS application.
Storage Conditions
2-8℃ for 2 years
Specification
|
Appearance |
Colorless to light brown liquid |
|
Activity |
≥800 U/ml |
|
Protein Concentration |
≥20 mg/ml |
|
Nickase |
None detected |
|
DNase |
None detected |
|
RNase |
None detected |
Properties
|
EC number |
3.4.21.64 (Recombinant from Tritirachium album) |
|
Isoelectric point |
7.81 |
|
Optimum pH |
7.0- 12.0 Fig. 1 |
|
Optimum temperature |
65 ℃ Fig. 2 |
|
pH stability |
pH 4.5- 12.5 (25 ℃, 16 h) Fig. 3 |
|
Thermal stability |
Below 50 ℃ (pH 8.0, 30 min) Fig. 4 |
|
Storage stability |
Over 90% activity for 12 month at 25 ℃ |
|
Activators |
SDS, urea |
|
Inhibitors |
Diisopropyl fluorophosphate; phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride |
Applications
1. Genetic diagnostic kit
2. RNA and DNA extraction kits
3. Extraction of non-protein components from tissues, degradation of protein impurities, such as DNA vaccines and preparation of heparin
4. Preparation of chromosome DNA by pulsed electrophoresis
5. Western blot
6. Enzymatic glycosylated albumin reagents in vitro diagnosis
Precautions
Wear protective gloves and goggles when using or weighing, and keep well ventilated after use. This product may cause skin allergic reaction and serious eye irritation. If inhaled, it may cause allergy or asthma symptoms or dyspnea. May cause respiratory irritation.
Unit definition
One unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme required to hydrolyze casein to produce 1 μmol tyrosine per minute under the following conditions.
Reagents preparation
Reagent I: 1g milk casein was dissolved in 50ml of 0.1M sodium phosphate solution (pH 8.0), incubated in 65-70 ℃ water for 15mins, stirred and dissolved, cooled by water, adjusted by sodium hydroxide to pH 8.0, and fixed volume 100ml.
Reagent II: 0.1M trichloroacetic acid, 0.2M sodium acetate, 0.3M acetic acid.
Reagent III: 0.4M Na2CO3 solution.
Reagent IV: Forint reagent diluted with pure water for 5 times.
Reagent V: Enzyme diluent: 0.1M sodium phosphate solution (pH 8.0).
Reagent VI: tyrosine solution: 0, 0.005, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1, 0.25 umol/ml tyrosine dissolved with 0.2M HCl.
Procedure
1. 0.5ml of reagent I is pre-warmed to 37℃, add 0.5ml of enzyme solution, mix well, and incubate at 37℃ for 10mins.
2. Add 1ml of reagent II to stop the reaction, mix well, and continue incubation for 30mins.
3. Centrifugate reaction solution.
4. Take 0.5ml supernatant, add 2.5ml reagent III, 0.5ml reagent IV, mix well and incubate at 37℃ for 30mins.
5. OD660 was determined as OD1; blank control group: 0.5ml reagent V is used to replace enzyme solution to determine OD660 as OD2, ΔOD=OD1-OD2.
6. L-tyrosine standard curve: 0.5mL different concentration L-tyrosine solution, 2.5mL Reagent III, 0.5mL Reagent IV in 5mL centrifuge tube, incubate in 37℃ for 30mins, detect for OD660 for different concentration of L-tyrosine, then obtained the standard curve Y=kX+b, where Y is the L-tyrosine concentration, X is OD600.
Calculation
2: Total volume of reaction solution (mL)
0.5: Volume of enzyme solution (mL)
0.5: Reaction liquid volume used in chromogenic determination (mL)
10: Reaction time (min)
Df: Dilution multiple
C: Enzyme concentration (mg/mL)
Figures
Fig.1 Optimum pH
100mM buffer solution:pH6.0-8.0, Na-phosphate; pH8.0-9.0, Tris-HCl; pH9.0-12.5, Glycine-NaOH.Enzyme concentration:1mg/mL
Fig.2 Optimum temperature
Reaction in 20 mM K-phosphate buffer pH 8.0.Enzyme concentration: 1 mg/mL
Fig.3 pH Stability
25 ℃, 16 h-treatment with 50 mM buffer solution: pH 4.5- 5.5, Acetate; pH 6.0-8.0, Na-phosphate; pH 8.0-9.0, Tris-HCl. pH 9.0- 12.5, Glycine-NaOH. Enzyme concentration: 1 mg/mL
Fig.4 Thermal stability
30 min-treatment with 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0.Enzyme concentration: 1 mg/mL
Fig.5 Storage stability at 25℃