Glucose Dehydrogenase(GDH)
Description
Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH) is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the reversible oxidative deamination of glutamate to a-ketoglutarate and serves as a key link between anabolic and catabolic pathways. In mammals, GDH is subject to allosteric regulation and has high activity in liver, kidney, brain, and pancreas. GDH activity in serum can be used to differentiate between liver diseases due to liver inflammation, which do not show elevated serum GDH activity, and diseases that result in hepatocyte necrosis, which results in elevated serum GDH.
GDH activity is determined by a coupled enzyme assay in which glutamate is consumed by GDH generating NADH, which reacts with a probe generating a colorimetric (450 nm) product proportional to the GDH activity present. One unit of GDH is the amount of enzyme that will generate 1.0 mmole of NADH per minute at pH 7.6 at 37 °C
Chemical Structure
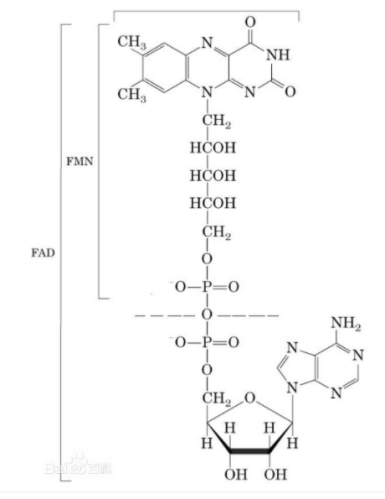
Reaction mechanism
D-Glucose + acceptor → D-Glucono-1,5-lactone + reduced acceptor
Specification
| Test Items | Specifications |
| Description | White amorphous powder, lyophilized |
| Activity | ≥160U/mg |
| Purity(SDS-PAGE) | ≥90% |
| Solubility(10 mg powder/mL) | Clear |
| Contaminating enzymes | |
| Glucose dehydrogenase (NAD) | ≤0.02% |
| Hexokinase | ≤0.02% |
| A-Glucosidase | ≤0.02% |
Transportation and storage
Transportation: Ice packs
Storage : Store at -25~-15°C(Long term), 2-8°C (short term)
Recommended re-test Life: 18 months